Agriculture technology (AgTech) has come a long way over the years. From traditional plowing and sowing techniques to today’s precision farming, the evolution of technology in agriculture has revolutionized the way we grow, harvest, and distribute food. With the world’s population continuously rising, there’s an increasing need to produce more food in a sustainable manner. This makes adopting new and modern farming technologies more important than ever.
What is Agriculture Technology?
Agriculture technology refers to the innovations, tools, and systems designed to enhance the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of agricultural operations. It involves both hardware and software applications tailored to meet the unique needs of the farming industry. Over time, agriculture technology has expanded to include automated machinery, sensor technologies, data analytics platforms, and much more.Types of Technology Used in Modern Agriculture:
- Software: Software solutions help farmers track data, predict outcomes, and manage resources. Examples include farm management software and precision farming platforms.
- Hardware: This category includes automated machinery, sensors, and tractor GPS systems used to collect data and perform tasks like planting, irrigation, and harvesting.
- Data-Driven Solutions: Tools like FJD Precision Agriculture Solution that leverages data, including satellite imagery, filed information, and sensor inputs, help optimize farming operations for maximum efficiency.
Key Areas of New Technology in Agriculture (2024 Trends)
1. Precision Farming with RTK Systems
Precision farming is all about using technology to increase crop yield while minimizing input costs. With tools like RTK Base Stations, farmers can achieve centimeter-level accuracy in their field operations. Real-time kinematic (RTK) GPS systems are projected to become standard on 60-70% of all new tractors and farm equipment sold by 2024. Technologies like the FJD V1 Base Station and similar systems help farmers precisely manage their planting, irrigation, and fertilization processes, reducing waste and improving yield. RTK systems also help manage large fields with precision, improving the efficiency of tractor operations and field machinery.
2. AI and Data Analytics in Crop Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used more in crop management, helping farmers analyze vast amounts of data from weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop performance. More than 30% of farms with over 100 acres are expected to implement AI-based tools for crop and soil monitoring, pest detection, and yield prediction by the end of 2024. AI systems can predict crop yields, optimize irrigation, and even detect early signs of pests or diseases. By using AI, farmers can make smarter decisions in real-time, ultimately saving time, resources, and money.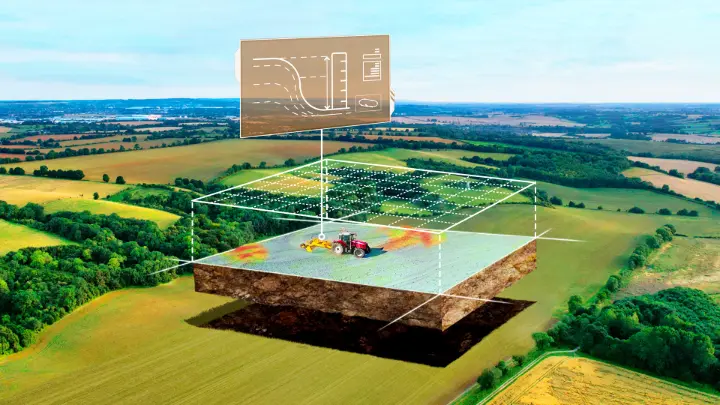
3. Blockchain for Farm-to-Table Transparency
Blockchain is not just for cryptocurrency. In agriculture, it’s being used to enhance transparency and traceability in the supply chain. More farmers and agri-businesses are turning to blockchain technology to track food from farm to table. This system allows consumers to trace the journey of their food, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud. It also improves food safety and helps farmers access new markets by offering more trust in their products.
4. Robotics for Soil Analysis and Harvesting
Robotics are increasingly being used in agriculture to perform tasks that require precision and speed, such as soil analysis and harvesting. The use of robotics will expand to even more tasks. Advanced robots can now pick delicate fruits and vegetables, sort crops, and help with field analysis. These robots are designed to handle crops gently, improving yield quality while reducing human labor costs.5. Sustainable and Regenerative Agriculture
Regenerative agriculture continues to rise in popularity as farmers focus on methods that restore soil health, sequester carbon, and boost biodiversity. Techniques like no-till farming, cover cropping, and agroforestry are now widely adopted to improve soil health. These practices not only help protect the environment but also lead to healthier, more productive farms over the long term.
6. Smart Irrigation Systems
Water conservation is a priority in modern agriculture. Smart irrigation systems, which use sensors to adjust watering schedules based on real-time data like soil moisture, weather forecasts, and crop needs, are becoming increasingly popular. These systems help reduce water usage, improve efficiency, and maintain crop health. As climate change leads to increased droughts in certain regions, smart irrigation technology is critical for preserving water resources and maintaining yields.
7. Automated Machinery for Harvesting and Planting
Automated machinery has evolved rapidly, offering farmers the ability to perform planting, cultivation, and harvesting tasks with minimal human intervention. Sales of autonomous tractors are expected to grow by 24% annually through 2024, as automation in farming reduces labor costs and increases efficiency. This technology uses RTK, GPS, and auto steer system to ensure precise seed placement, optimal planting depth, and even harvesting. Automated harvesters can work continuously day or night, drastically improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.8. Vertical Farming and Hydroponics
Urban agriculture is making strides, and vertical farming is at the forefront of this movement. In 2024, we’re seeing more farms move indoors and grow crops in stacked layers using hydroponic or aeroponic systems. This method uses less water, land, and energy, making it possible to grow fresh produce in cities and urban environments. As demand for sustainable food production increases, vertical farming is poised to become a major player in the global food supply chain.9. IoT in Agricultural Machinery
The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to play a significant role in modern farming. The global Internet of Things (IoT) in agriculture market is projected to grow to $34.9 billion by 2024, with a CAGR of 19.5%. By embedding sensors and smart devices in tractors, combines, and other equipment, farmers can track performance and get real-time insights. IoT sensors can monitor fuel consumption, engine performance, soil conditions, and crop health. This data helps farmers optimize their machinery usage, reduce downtime, and increase efficiency.10. 3D Printing for Farm Equipment and Parts
3D printing has made its way into agriculture, and in 2024, it’s becoming more common for farmers to print spare parts for their equipment, such as tractors and harvesters. 3D printing reduces downtime by allowing farmers to print parts on-site, avoiding the delays and costs associated with shipping and ordering replacement parts. This trend also helps farmers customize equipment to meet specific needs on their farm.The Benefits of Modern Agriculture Technology
Modern AgTech is bringing numerous benefits to farmers worldwide. Here are some of the most significant advantages:Increased Efficiency
Technology has drastically reduced the time spent on manual tasks. Automated tractors, seeders, and harvesters can work round-the-clock with minimal human supervision. Technologies like RTK systems provide precise guidance for tractors, allowing them to perform tasks with pinpoint accuracy.Improved Yields
With precision farming techniques, farmers can optimize crop growth and increase yields. Tools like soil sensors, AI-driven crop management systems, and biotechnology contribute to higher productivity, enabling farmers to get more from their land.Cost Savings
Agricultural technology helps reduce input costs, such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides. By analyzing real-time data from various sources, farmers can apply inputs more efficiently, saving money in the long run. For example, precision irrigation systems deliver the right amount of water to crops, reducing waste and lowering water bills.Sustainability
Modern technologies allow farmers to adopt more sustainable practices. From water conservation techniques to using fewer chemicals, AgTech plays a key role in making farming more environmentally friendly. Systems that optimize water usage, like smart irrigation, reduce the environmental impact of farming while ensuring crops remain healthy.Reduced Environmental Impact
Using technology like automated machinery and sensors helps reduce overuse of resources such as water and fertilizers. This not only minimizes waste but also decreases emissions associated with farm equipment.Challenges and Barriers to Adopting New Agricultural Technology
While the benefits of modern agriculture technology are clear, there are also some challenges and barriers that farmers must overcome when adopting these new solutions.Cost of Technology
The initial investment required for AgTech solutions can be high, which makes it difficult for some farmers, especially small-scale ones, to adopt them. However, over time, the return on investment (ROI) through increased yields and savings on inputs can make these technologies worthwhile.Technology Adoption by Small-Scale Farmers
Small-scale farmers may struggle with the cost and complexity of implementing new technologies. Lack of training, inadequate resources, or limited access to financing can make it harder for them to take full advantage of AgTech.Data Management and Privacy
Data is an essential component of modern agriculture technology. However, the collection, storage, and use of farm data raise concerns about privacy and security. Farmers need to be confident that their data is being handled securely by technology providers.Connectivity Issues
In rural areas, limited access to high-speed internet can hinder the use of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, cloud-based solutions, and real-time data sharing. This lack of connectivity can limit the effectiveness of certain AgTech systems, particularly those that rely on cloud computing or remote data transfer.The Evolution of Agriculture Technology: From 1.0 to 5.0
Agriculture technology has evolved in distinct phases over the past century. Here’s a look at how the field has progressed, from basic farming tools to today’s sophisticated systems.Agricultural Revolution 1.0 (Pre-Industrial Agriculture)
The first phase of agricultural technology revolved around simple tools like hoes, plows, and animal-powered carts. Farming was manual, and output was limited by human labor and natural resources. However, the domestication of animals and early irrigation systems marked a significant step forward in human agriculture. This was an era where farmers relied on traditional methods passed down over generations.Agricultural Revolution 2.0 (Industrial Revolution)
In the 18th and 19th centuries, the Industrial Revolution brought mechanization to farming. Steam-powered machines like plows, harvesters, and threshers replaced manual labor, dramatically increasing efficiency and output. This era also saw the introduction of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, which boosted yields and allowed farms to grow larger. During this time, the tractor replaced oxen as the primary source of field power.Agricultural Revolution 3.0 (Green Revolution and Modern Technologies)
The Green Revolution of the 1940s to 1960s introduced high-yielding varieties of crops, chemical fertilizers, and advanced irrigation systems that transformed agriculture worldwide. This period also saw the advent of early computers and data analysis in agriculture. Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) were introduced, leading to significant improvements in crop resistance to pests and diseases. The mechanization of farming continued, and the digital age began to make its way into agriculture.Agricultural Revolution 4.0 (Digital and Precision Agriculture)
The 4th agricultural revolution, also known as the digital farming revolution, is defined by the integration of digital technologies like big data, AI, IoT, and precision farming tools. Farmers now have access to satellite imagery, drones, and sensors that allow them to monitor every aspect of their crops in real-time. Systems like the FJD Auto Steer System enable precision farming down to the centimeter, optimizing yields, reducing waste, and cutting input costs. Automated machinery, advanced irrigation systems, and crop management software are standard on many modern farms.Agricultural Revolution 5.0 (Sustainable and Resilient Farming)
Agriculture 5.0 is about combining the latest technological advancements with sustainable farming practices. This next phase emphasizes not just efficiency, but also environmental stewardship. In 2024, we are seeing the rise of regenerative agriculture, carbon sequestration, and precision sustainability. Technology continues to play a role, but now there’s a growing focus on improving soil health, reducing carbon footprints, and using fewer chemicals.How to Incorporate Modern Agricultural Technology into Your Farm
Assessing Farm Needs:
Before implementing new technologies, it's essential to evaluate your farm’s size, crops, and resources. Understanding what technology best suits your farm's specific needs will help you make informed decisions.
Choosing the Right Tools and Equipment:
Once you know what your farm requires, the next step is selecting the right tools. From farm management system to automated system, there's a wide range of equipment to choose from. It’s important to prioritize technologies that will deliver the highest ROI for your farm.
Training and Support:
Farm workers must be trained to use these new tools effectively. Many AgTech companies offer workshops and training programs to help farmers get the most out of their technology.
Steps for Implementation:
Start by trialing small-scale technology solutions and evaluating their effectiveness. Once you see positive results, scale up your technology adoption to improve operations across the entire farm.